How Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are Transforming Industries 1
AMRs and AGVs are automating the handling and transportation of materials, enhancing operational efficiency and safety, and reshaping the way a variety of industries operate. This includes everything from manufacturing, warehousing and logistics, to aerospace, medicine and even mining.
- AMRs are smart, self-driving robots that use sensors, cameras, and real-time data to navigate and plan routes dynamically. AMRs excel in scenarios where adaptability and scalability are vital, such as dynamic warehouse operations or hospital patient care.
- AGVs, on the other hand, follow predetermined paths created by guidance systems like magnetic strips or lasers. They are best suited for environments where tasks are repetitive and the movement patterns do not change often, such as in assembly lines or standardized material handling in factories.
Ensuring Safe and Optimal Performance: Why Load Monitoring Matters for AMRs / AGVs
- Total Load Verification systems employ load cells to measure and verify that the weight is within safe operational parameters prior to start of operation. This prevents overloading that could cause accidents and lead to mechanical failures.
- Tip-Over Prevention systems utilize advanced Center of Gravity (COG) monitoring to measure weight distribution and confirm that it is within safe limits. A sufficiently off-center weight distribution can strain the robot’s motor and structural integrity, reducing stability and increasing wear and tear. If the system detects an out of bounds center of gravity, it initiates safety measures such as alerting the operator or bringing the vehicle to a halt to prevent tip-overs.
Solutions for AMR/AGV Load Monitoring
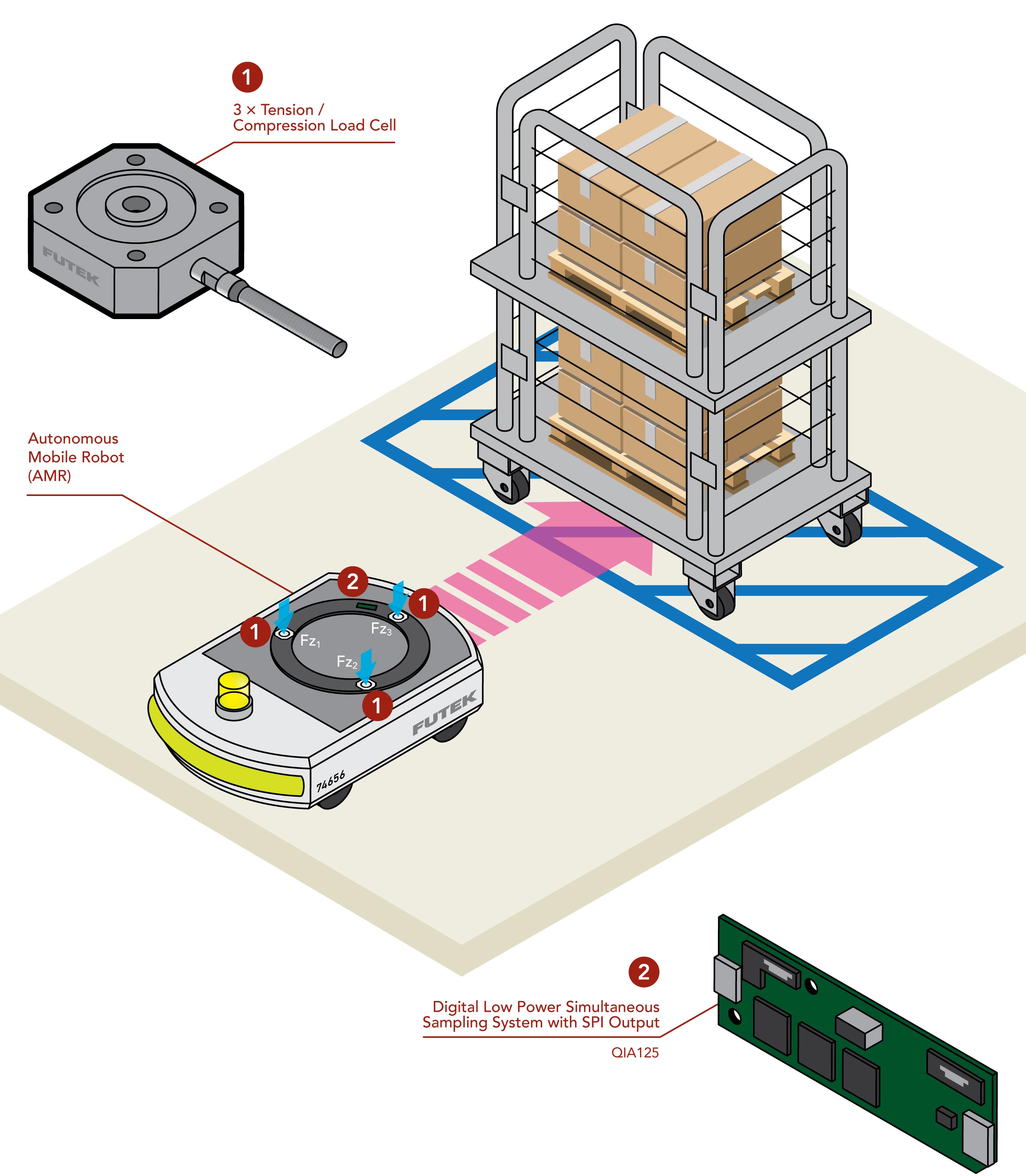
FUTEK has drawn on decades of customized sensor design experience to develop a system that combines multiple Tension/Compression Load Cells to monitor total load as well as weight distribution. Combined with FUTEK’s in-house designed Digital Signal Conditioner, this system allows the AMR/AGV to respond in real-time to excessive or uneven load.
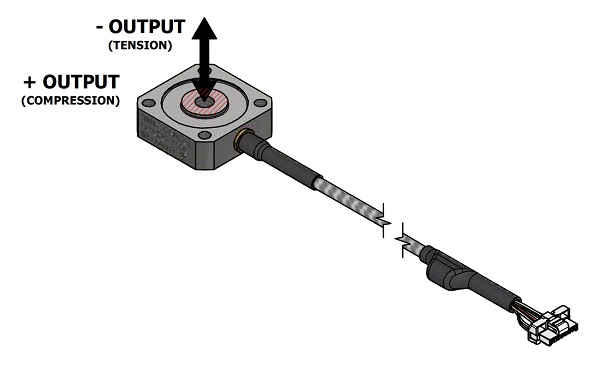
- FUTEK load cells, such as the QLA428 Square Flange Diaphragm Load Cell (#1 in figure) are arranged in a triangular system that monitors the total load and weight distribution and provides realtime feedback to AMR/AGV’s microcontroller. The system’s ability to measure vertical forces (Fz) at three different points (Fz1, Fz2, Fz3) is important for accurate center of gravity calculations. Any imbalance or overload is immediately detected, allowing the AMR/AGV to take corrective action, thus maintaining stability and operational safety.
- FUTEK’s QIA125 Low Power Three Channel SPI Output Digital Signal Conditioner (#2 in figure) converts the mV/V analog signal of the Tension/Compression Load Cells which enables seamless integration with the AMR/AGV’s onboard control system. This Multi-Channel Signal Conditioner can interface with up to three separate Load Cells simultaneously and supports SPI/UART with low power consumption. QIA125’s high-speed data communication provides a sampling rate of up to 4,800 SPS and 18.1 Bits Noise Free Resolution (NFR) which enables real-time feedback for load monitoring and control.
FUTEK's multidisciplinary engineering team can further customize the Load Monitoring System according to application needs, accounting for environmental variables (high vibration/shock, extreme temperatures), unusual sensor geometries, and output requirements. FUTEK’s robust framework for load management ensures that AMRs and AGVs can perform optimally in a safe manner, making them invaluable assets in the increasingly automated landscape of modern industries.
Contact Us
Please Contact Us with questions.
How Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are Transforming Industries 1
AMRs and AGVs are automating the handling and transportation of materials, enhancing operational efficiency and safety, and reshaping the way a variety of industries operate. This includes everything from manufacturing, warehousing and logistics, to aerospace, medicine and even mining.
- AMRs are smart, self-driving robots that use sensors, cameras, and real-time data to navigate and plan routes dynamically. AMRs excel in scenarios where adaptability and scalability are vital, such as dynamic warehouse operations or hospital patient care.
- AGVs, on the other hand, follow predetermined paths created by guidance systems like magnetic strips or lasers. They are best suited for environments where tasks are repetitive and the movement patterns do not change often, such as in assembly lines or standardized material handling in factories.
Ensuring Safe and Optimal Performance: Why Load Monitoring Matters for AMRs / AGVs
- Total Load Verification systems employ load cells to measure and verify that the weight is within safe operational parameters prior to start of operation. This prevents overloading that could cause accidents and lead to mechanical failures.
- Tip-Over Prevention systems utilize advanced Center of Gravity (COG) monitoring to measure weight distribution and confirm that it is within safe limits. A sufficiently off-center weight distribution can strain the robot’s motor and structural integrity, reducing stability and increasing wear and tear. If the system detects an out of bounds center of gravity, it initiates safety measures such as alerting the operator or bringing the vehicle to a halt to prevent tip-overs.
Solutions for AMR/AGV Load Monitoring
FUTEK has drawn on decades of customized sensor design experience to develop a system that combines multiple Tension/Compression Load Cells to monitor total load as well as weight distribution. Combined with FUTEK’s in-house designed Digital Signal Conditioner, this system allows the AMR/AGV to respond in real-time to excessive or uneven load.
- FUTEK load cells, such as the QLA428 Square Flange Diaphragm Load Cell (#1 in figure) are arranged in a triangular system that monitors the total load and weight distribution and provides realtime feedback to AMR/AGV’s microcontroller. The system’s ability to measure vertical forces (Fz) at three different points (Fz1, Fz2, Fz3) is important for accurate center of gravity calculations. Any imbalance or overload is immediately detected, allowing the AMR/AGV to take corrective action, thus maintaining stability and operational safety.
- FUTEK’s QIA125 Low Power Three Channel SPI Output Digital Signal Conditioner (#2 in figure) converts the mV/V analog signal of the Tension/Compression Load Cells which enables seamless integration with the AMR/AGV’s onboard control system. This Multi-Channel Signal Conditioner can interface with up to three separate Load Cells simultaneously and supports SPI/UART with low power consumption. QIA125’s high-speed data communication provides a sampling rate of up to 4,800 SPS and 18.1 Bits Noise Free Resolution (NFR) which enables real-time feedback for load monitoring and control.
FUTEK's multidisciplinary engineering team can further customize the Load Monitoring System according to application needs, accounting for environmental variables (high vibration/shock, extreme temperatures), unusual sensor geometries, and output requirements. FUTEK’s robust framework for load management ensures that AMRs and AGVs can perform optimally in a safe manner, making them invaluable assets in the increasingly automated landscape of modern industries.